Abkhazians & Ossetians in Georgia. A Short History
In light of the disinformation campaign carried out by Russian information networks and picked up by western media, the Institute of the Georgian History at Ivane Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University has released an explanation as to why the Abkhazia and Tskhinvali regions (incorrectly called "South Ossetia") have always been an integral part of Georgia.
In the remote past, to the south of the Great Caucasian Range and east of the Black Sea, rural clans fought each other for land and mines, making alliances and early states. Two cultures equipped first with bronze and then with iron were established in the valleys of the rivers Rioni (Phasis), Chorokhi (Aphsaros), and Mtkvari (Cyros/Kura). Roughly, the borders of Colchis included the city of Pitius (Bichvinta, Pitsunda) in the North West, Sarapanis (Shorapani) in the East, near the Likhi mountains, which divides Georgia into West and East, and the mouth of the river Chorokhi in the South, near Batumi, Georgia’s main port. Another name for Colchis is Egrisi, derived from the tribal name Margali/Megreli/Mingrelian. The Mingrelian language, very close to the Georgian, is still spoken in West Georgia as a family one, like that of West Georgian highlanders, the Svani. The next country had two rivers, Chorokhi, now mostly in Turkey, and Mtkvari within its borders. Local folk called it Kartli, and the Greeks – Iberia and Iberians. The latter term contributes to Ivirk, Vrastan – Armenian terms; also to Varkan, Gurgan, Gurgistan – Persian terms, which in turn contributes to Georgia and Gruziya.
Thus, Kartli, while comprising the Mtkvari and Chorokhi valleys, was labeled as Iberia, or Vrastan, or Varkan, or Gurgan by foreigners. Gradually, Colchis/Egrisi and Kartli/Iberia became more and more integrated, and Georgian, the language spoken in Kartli, spread to the eastern Black Sea coast, putting the Mingrelian and Svani languages in the position of a family language. From that point on, this new country was called Sakartvelo, a term derived from Kartli, and also Iberia, Gurgistan, Gruziya and Georgia (T. Dundua. History of Georgia. Tbilisi. 2017, pp. 5-22. v. Academia.edu/Tedo Dundua).
Still, there was another language in West Georgia which was also converted into a family language: Abkhazian. The Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia (Georgia) has Sokhumi as its capital. Sokhumi is the Turkish version of the Georgian name Tskhumi, while the Greeks and Italians called the city Dioscurias and Sebastopolis. People living in its neigborhood in the Classical and Hellenistic periods were the Colas and the Coraxae, obviously Colchian clans. Their names are substituted by that of the Colchians themselves. The first mention of the Aphsils, obvious ancestors of the Abkhazians, near Sebastopolis/Tskhumi, dates back to the 70s of the 1st c. A.D. Soon, their relatives, the Abasks, appear. These two names sometimes disappear in favor of “Lazi,” the name of Mingrelian-speaking people descended from the southern mountains to mingle with the Colchians, thus changing the name of the country into Lazica. In the northern part of Lazica under the local feudal lords, they again call themselves Aphsils and Abasks, when unified with the rest of the country – Lazi. That means that from the 2nd c. A.D., the Mingrelian language was a social one throughout Lazica, while the Abkhazian language was put in the position of a family language spoken near Sebastopolis/Tskhumi. Indeed, the special Mingrelian term for that part of Lazica was “apkha,” i.e. periphery. The periphery of what? That of Mingrelian, i.e. western Georgian, culture. Gradually, Aphsils and Abasks under the local princes also started to call themselves Abkhazians. When in the 8th c., apparently through marriage, their prince found himself residing in the central city of Kutaisi, Lazica/Egrisi received one more name – Apkhazeti. With the Georgian language becoming dominant on the eastern Black Sea coast, the Mingrelian, Svani and Abkhazian languages found themselves in the position of a family language (T. Dundua. Christianity and Mithraism. The Georgian Story. Tbilisi. 1999, p. 6; T. Dundua, Akaki Chikobava. Pacorus, the Lazi King, Who Was Overlord of Colchis/Western Georga. Tbilisi. 2013, pp. 9-16; T. Dundua. Georgia within the European Integration. Tbilisi. 2016, pp. 81-88. v. Academia.edu/Tedo Dundua).
West and East unified was called Sakartvelo/Georgia. And the title of the kings from the Bagrationi ruling dynasty was as follows: “King of the Abkhazians (i.e. Western Georgia), Kartvelians (Eastern and Southern Georgia), Ranians and Kakhetians (extreme East of the Eastern Georgia)” (T. Dundua. Review of Georgian Coins with Byzantine Iconography. Quaderni ticinesi di numismatica e antichità classiche. Lugano. 2000. Vol. XXIX, pp. 389-393; T. Dundua and Others. Online English- Georgian Catalogue of Georgian Numismatics).
The decline of Georgia towards the end of the 16th c. enabled the Ottomans to increase their territory, seeing them taking control of the cities on the eastern Black Sea coast. Georgian frontier defenses were down. Finding so little opposition, many tribes settled in the districts they had penetrated, a new wave of the Abkhazian speaking clans among them. They made their way from the mountains first to the region of nowadays Sochi (Russian Federation), and then down the coast towards Bichvinta (Pitius, Pitsunda). Those rough highlanders forced part of the local agricultural folk to flee to the central regions. Thus, rural and urban sites suffered much and the links with the rest of the country were badly damaged. The Ottoman overlords also encouraged the slave trade, completely changing the economic visage of the northwest of western Georgia for centuries before the Russians advance against the Ottomans in the 19th c. (T. Dundua. North and South (towards the Question of the NATO enlargement). www.nato.int/acad/fellow/99-01/dundua.pdf, pp.41-42; T. Dundua and Others. The Black Sea – Zone of the Contacts. Tbilisi. 2001, pp. 9-10, 15-16; T. Dundua and Others. The Black Sea. A History of Interaction. Teaching Pack. The Council of Europe. Oslo. 2004, pp. 46, 105. v. Academia.edu/Tedo Dundua).
The Russian Empire annexed eastern Georgia, the Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti, in 1801. This paved the way for Russian expansion into western Georgia. In 1810, Abkhazian prince Giorgi (Safar Beg) Shervashidze swore allegiance to the Russian Emperor and in 1864, Russian governance was established in the territory. (Abkhazia in the late 18th- early 19th centuries. Entry of Abkhazia Under the “Protection” of Russia. in Essays from the History of Abkhazia. Tbilisi. 2011, pp. 300-305). Sukhumi military department was founded (M. Lordkipanidze. The Abkhazians and Abkhazia (Georg., Russ. and Engl. texts). Tbilisi. 1990 http://www.amsi.ge/istoria/div/m.lordkiPaniZe_afx.html#90).
Although the process of separating Abkhazia from Georgia was actively supported by the Russian authorities, still Abkhazia was a natural and integral part of Georgia. Perhaps it was for this reason that the Sukhumi military district was soon included in the Kutaisi governorate. Despite the negative effects of the Russian imperial policy, in 1918, the year when the Democratic Republic of Georgia was founded, Abkhazia was a part of Georgia (M. Lordkipanidze. The Abkhazians and Abkhazia (Georg., Russ. and Engl. texts). Tbilisi. 1990 http://www.amsi.ge/istoria/div/m.lordkiPaniZe_afx.html#90).
On June 11, 1918, an agreement was signed between the people’s council of Abkhazia and the leadership of the Democratic Republic of Georgia, where Abkhazia as a part of Georgia gained autonomy.
After the end of Georgia’s short independence in 1921, Abkhazia remained within Soviet Socialist Republic of Georgia under a special union agreement, as a treaty republic having a certain type of autonomy within Georgia. In 1931, Abkhazia officially became the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (ASSR) of Georgia (Political Status of Abkhazia within the Soviet Georgia. 1921-1937. in Essays from the History of Abkhazia. Tbilisi. 2011, pp. 419-436; Революционные комитеты Абхазии в борьбе за установление и упрочение Советской власти. Сборник документов и материалов. Сухуми. 1961, p. 350). This remained unchanged until the end of the Soviet Union. According to the 1989 Soviet census, the total population on the territory of the ASSR of Abkhazia was 525,061, of which 239,872 were ethnic Georgians (45.7% of the population), while 93,267 were Abkhazians (17.8%) (S. Markedonov. Abkhazia: Historical Context. in Abkhazia Between Past and Future. Prague. 2013, p. 18).
Abkhazia enjoyed cultural and scientific benefits as part of Georgia during the Soviet era. The Abkhazian language was taught at the schools, and university.
Since 1993, the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia has been occupied by the Russian Federation (for the full-length narrative about Abkhazians v. З. Папаскири. Абхазия: история без фальсификации. 2е изд. Тбилиси. 2010 (with Engl. summary).
The next region occupied by the Russian Federation was the Autonomous District of South Ossetia. The Ossetians started settling in Georgia beyond the Caucasian range in the 16th-17th cc. as fugitives.
After the annexation of eastern Georgia by Russia in 1801, the Ossetian villages were attached to the Gori district of the Tbilisi governorate.
In 1920, the Russian Bolsheviks supported Ossetians living in the Democratic Republic of Georgia, in the mountains north of Gori, to establish the Soviet power there and declare the territory a part of Soviet Russia. This was an abortive attempt.
In February 1921, Soviet Russia violated the agreement of May 7, 1920 by militarily attacking the Georgian state and eliminating its independence. In April 1922, the Bolsheviks granted so-called South Ossetia the status of autonomous district within Soviet Socialist Republic of Georgia. Soviet policy can be regarded as a premeditated attempt to disrupt the future attempts of the Georgians to gain independence and build a stable state as separatism within Georgia would constrain Tbilisi in its actions. The Autonomous District of South Ossetia consisted of a number of Ossetian settlements and a purely Georgian town Tskhinvali.
Thus, in 1922, the Autonomous District of South Ossetia was created in the heart of historic Georgian lands where the Georgian population represented the majority of the population.
It also needs to be emphasized that throughout the Soviet period (until 1991), the Ossetians living in Georgia were granted all necessary legal rights as an ethnic minority. Then Georgia became independent and the Russian occupation of the Autonomous District of South Ossetia began. (M. Lordkipanidze, G. Otkhmezuri. Ossets in Georgia. in The Caucasus and Globalization. Vol. 1 (4). Tbilisi. 2007, pp. 109-118; R. Topchishvili. Ethnic Processes in Shida Kartli (the Ossetians in Georgia). in Causes of War – Prospects for Peace. Georgian Orthodox Church. Konrad-Adenauer-Foundation. Tbilisi. 2009, pp. 111-138).
Prof. Dr. Tedo Dundua is the Director of the Institute of Georgian History, Faculty of Humanities, at the Ivane Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University.
By Prof. Dr. Tedo Dundua & Dr. Emil Avdaliani
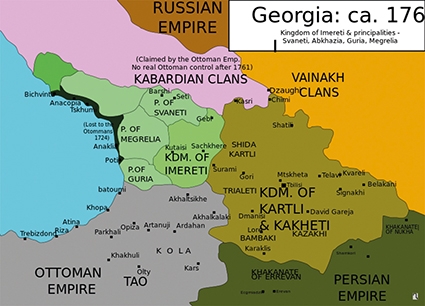
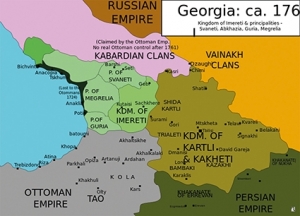
Photo: Map of Georgian states in 1762. Based on the map of Dr. Andrew Andersen, from Atlas of Conflicts. Author: Gaeser